Chiroteuthis
Clyde F. E. Roper and Richard E. Young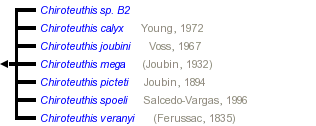

This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxIntroduction
Species of Chiroteuthis are the most commonly encountered species of the family. They possess a variety of photophores that can produce some unusual bioluminescent displays. The title photograph shows the series of photophores along the ventral arms, the rows of photophores on the ventral surface of the eyes (the arrangement of ocular photophores, however, varies with the species) and the visceral photophores (absent in C. mega). The tentacles carry a series of complex, peculiarly constructed, pad-like photophores along the tentacular stalk that distally are mostly embedded in the aboral surface of the club. The last member of this photophore series, the club-tip photophore, however, is greatly enlarged and possesses muscular lids that open and close over the organ. The function(s) of these photophores are unknown although the club-tip photophore could act as a lure to attract prey (Voss, 1956). The very long tentacles can be completely retracted into elongate tubes formed by the broad lateral membranes (=tentacular sheath) of the fourth arms. Arms IV (the ventral arms) are not only much longer but, also, thicker than the other arms. The tentacular clubs are distinctive at the generic level and often at the specific level. The large fourth arms contain many large vesicles that hold ammonium chloride. This low-density fluid apparently, is responsible for the typical oblique orientation of the squid with the arms uppermost, as observed from submersibles and as shown in the title photograph on the family page.
Diagnosis
A chiroteuthid ...
- with suckers on both proximal and distal regions of club.
- with typical tragus and antitragus on funnel locking-apparatus.
- with a row of photophores along each arm IV.
Characteristics
- Arms
- Arms IV much the longest and greatly thickened.
- Tentacles
- Suckers in four series throughout club.
- Head
- Olfactory organ located on stalk just posterior to each eye.
- Funnel
- Funnel valve present.
- Locking-apparatus oval with typical tragus and antitragus.
- Photophores
- A series of silver photogenic spheres extends along arms IV (each photophore alternates with a lateral arm sucker).
image info
Figure. Oral view of a portion of the abraided arm IV of C. picteti, Hawaiian waters. Each spherical Arm IV photophore (arrows) is covered with chromatophores and paired with a sucker from the dorsal series on the arm (the middle sucker of the ventral series was lost during capture). Also note the broad lateral membrane (=tentacular sheath) at the base of the arrows. Photograph by R. Young.
- Visceral photophores present in all but one species.
- Ocular photophores present as stripes or series of round organs or combination of both.
- Pad-like photophores present on tentacular stalk, distally embedded in club.
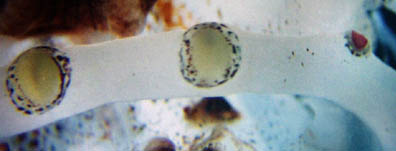 image info
image info Figure. View of three pad-like tentacle-stalk photophores of C. picteti. Note that one is small and has a violet pigmentation. We do not know if this is normal or a result of loss and regeneration. See also the pad-like photophores of Asperoteuthis. Photograph by R. Young.
- Large club-tip photophore.
- Numerous small photophores on oral surface of distal tentacular stalk.
image info
Figure. Oral view of the tentacle-stalk at base of the club of Chiroteuthis sp., Hawaiian waters. The arrow points to one of many small, light-colored photophores present on the stalk but often difficult to detect.
- A series of silver photogenic spheres extends along arms IV (each photophore alternates with a lateral arm sucker).
Discussion of Phylogenetic Relationships
A cladistic analysis has not been done on this group. Nevertheless, the species can be grouped provisionally on the basis of the following characters.
Group 1: C. picteti, C. mega
- Ocular photophores in three series/stripes on the eyeball.
- Clubs long with protective membranes in two sections with length:length ratios of > 1:8.
- Distal section with broad, triangular, closely-spaced trabeculae.
- All pigment on clubs in chromatophore organs rather than epithelial cells.
- One large central tooth on club sucker rings.
Group 2: C. joubini, C. spoeli, C. sp. B2.
- Ocular photophores in two series on the eyeball.
- Clubs short with protective membranes in three sections.
- Distal section with narrow, broadly spaced trabeculae.
- Much pigment on clubs in epithelial cells rather than chromatophores.
- No large central tooth on club sucker rings.
Group 3: C. veranyi, C. calyx
- Ocular photophores in two stripes and several round photophores.
- Club short with protective membranes in two, nearly equal, sections.
- One large central tooth on club sucker rings.
Speciation in Chiroteuthis
Within each of the three groups there exists considerable unexplained variation. Our knowledge of speciation in this group is minimal. Future detailed evaluation of the variation could indicate that some of the species recognized above will be synonymized (e.g., all forms in the C. joubini group could represent a single, highly variable species) or that additional new species will be recognized within the forms now known. We caution anyone against naming species in this genus until a better understanding of the variability is known.
Life History
The late doratopsis stages of the paralarval period have tentacles that possess a distal, expanded, paralarval club and a proximal presumptive (developing) adult club. The latter has four series of very small suckers which are more regularly arranged and extensive than in paralarvae of the other genera except New Genus B.
 image info
image infoFigure. Oral view of a tentacle from an unidentified 28 mm ML doratopsis. The paralarval club has large suckers and a keel (but without division into manus and dactylus); the developing adult club on the tentacular stalk has small suckers. Drawing from Roper and Young, 1967.
All members of the family lack hectocotylized arms. Species of Chiroteuthis, at least, have an elongate penis that can extend beyond the mantle opening and probably compensates for the absence of a hectocotylus.
Figure. Ventral view of the viscera of a mature male Chiroteuthis sp. with the long, slender penis extending to the right. A relatively small gill lies beneath the penis. The testis is white as are the spermatophores within Needham's sac to the right of the testis. The insert to the right shows the penis at a different angle where the broad, flat tip is more apparent. Also seen are the large visceral photophores and the violet renal appendages.
Distribution
Within two of the species groups, geographical distributions appear to be non-overlapping although the data records are few for all species.
In the C. veranyi group, C. veranyi is known from the Atlantic and Indian Oceans and in the Pacific Ocean from the South and Equatorial Pacific. C. calyx is known only from the temperate and boreal North Pacific.
In the C. picteti group, C. picteti is known from the tropical and subtropical Indo-eastern Pacific while C. mega is known from the Atlantic Ocean, the western Pacific and the temperate South Pacific waters off New Zealand.
In contrast different distribution patterns do not separate all members of the C. joubiniChiroteuthis spoeli group. is known from the tropical Pacific and the tropical south Atlantic to the temperate North Atlantic and the western Indian Ocean. Chiroteuthis. sp. B2 is known from the subtropical and temperate South Atlantic. C. joubini is known from the subtropical North and temperate South Atlantic.
References
Chun, C. 1910. Die Cephalopoden. Oegopsida. Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse der Deutschen Tiefsee-Expedition, "Valdivia" 1898-1899, 18: 1-522 + Atlas.
Hunt, J. C. 1996. The behavior and ecology of midwater cephalopods from Monterey Bay: Submersible and laboratory observations. Ph. D. Dissertation, Univ. Calif. Los Angeles. 231 pp.
Vecchione, M., B. H. Robison, and C. F.E. Roper. 1992. A tale of two species: tail morphology in paralarval Chiroteuthis (Cephalopoda: Chiroteuthidae). Proceeding of the Biological Society of Washington 105(4): 683-692.
Roper, C. F. E. and R. E. Young (1967). A review of the Valbyteuthidae and an evaluation of its relationship with the Chiroteuthidae. Proc. U.S. Nat. Mus., 123: 1-9.
Voss, G. L. 1956. Review of the cephalopods of the Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Mar. Sci. Gulf Carib. 6: 85-178.
Young, R. E. (1991). Chiroteuthid and related paralarvae from Hawaiian waters. Bull. Mar. Sci., 49: 162-185.
About This Page
Richard E. Young
Dept of Oceanography
University of Hawaii
Honolulu, Hawaii 96822
USA
Page copyright © 1998 and Richard E. Young
Citing this page:
Roper, Clyde F. E. and Young, Richard E. 1998. Chiroteuthis . Version 01 January 1998 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Chiroteuthis/19462/1998.01.01 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/