Caeciliusidae
Emilie Bess and Kevin P. Johnson

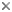
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxIntroduction
Caeciliusidae (formerly called Caeciliidae) contains about 600 described species in more than 35 genera. The family is distributed worldwide with most diversity in Asia and Africa. There are about 35 species of the family in North America.
Caeciliusids are small to medium-sized bark lice (~3 mm in length). Body color is generally yellow. Caeciliusids are leaf-inhabiting bark lice that live on conifers and broad-leaf trees. Most are long-winged, but some of the few ground litter species have both long- and short-winged females. This is the largest family of leaf-inhabiting bark lice.
Characteristics
Synapomorphies
None.
General Characters
- Head:
- Head is short.
- Antennae have 13 segments.
- Ocelli are grouped on a tubercle.
- Mandibles have an open appearance:
- usually elongate and hollowed out posteriorly
- to accommodate large, bulging galae (cheeks).
- Legs:
- Tarsi have 2 segments.
- Wings:
- Forewing:
- Veins Rs and M are often fused for part of length.
- Areola postica is free.
- Branches of veins have a singe row of hairs.
- Margin has more than one row of hairs.
- Marginal hairs do not cross one another as in Pseudocaeciliidae.
- Vein CuP may be have hairs or not.
- Wing membrane is nearly always hairless.
- Hindwing margin has hairs all around except basal 2/3 of front margin.
- Abdomen:
- Abdomen has vesicles (inflatable sacs) that excrete a sticky substance, used to adhere insect to substrate.
- Male:
- Hypandrium is simple.
- Phallosome is closed anteriorly with rugose sclerification on penial bulb.
- Female: Gonapophyses are reduced:
- Dorsal valve is usually slender.
- Ventral valve is usually slender.
- External valve is reduced to small sclerotised area with 0,1, or 2 hairs.
- Eggs:
- Eggs are smooth, laid in groups, and covered with silken strands.
How to Know the Family
- Small to medium-sized bark lice (~3 mm in length).
- Characteristic yellow color.
- Head is short.
- Ocelli are grouped on a tubercle.
- Tarsi have 2 segments.
- Mandibles have an open appearance, usually elongate and hollowed out posteriorly to accommodate large, bulging galae (cheeks).
- Labial palps are often somewhat triangular & protruding.
- Abdomen has vesicles (inflatable sacs) that excrete a sticky substance used to adhere insect to substrate.
Discussion of Phylogenetic Relationships
Caeciliusidae is one of the best studied families within Psocomorpha, due primarily to morphological work by E. L. Mockford. Recent studies, however, have revealed that Caeciliusidae is not monophyletic. While molecular data strongly supported the monophyly of the infraorder Caeciliusetae, the Caeciliusidae taxa included in the analysis (10 species in 8 genera) are scattered throughout the infraorder (18S nDNA; Johnson et al. 2004). An analysis of 12S, 16S, COI mtDNA and 18s nDNA that included two Caeciliusidae genera also showed a paraphyletic relationship, with Valenzuela and Xanthocaecilius grouped with a species of Stenopsocidae (Johnson & Mockford 2003). Morphological analysis of the Caeciliusidae also indicates paraphyly, with no synapomorphic characters supporting the family (Yoshizawa 2002).
References
Johnson, K. P. & E. L. Mockford. 2003. Molecular Systematics of Psocomorpha (Psocoptera). Systematic Entomology 28: 409-40.
Johnson, K. P., K. Yoshizawa, and V. S. Smith. 2004. Multiple origins of parasitism in lice. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B 271:1771-1776.
Lienhard, C. and C. N Smithers. 2002. Psocoptera (Insecta) World Catalogue and Bibliography. Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle, Geneva, Switzerland.
Mockford, E. L. 1993. North American Psocoptera (Insecta). Gainesville, Florida: Sandhill Crane Press.
Mockford, E. L. 1999. A Classification of the Psocopteran Family Caeciliusidae (Caeciliidae Auct.). transaction fo the American Entomological Society 125: 325-417.
Smithers, C. N. 1996. Psocoptera. Pp. 1-80, 363-372 (Index) in Wells A. (ed.) Zoological Catalogue of Australia. Vol. 26. Psocoptera, Phthiraptera, Thysanoptera. Melbourne: CSIRO Publishing, Australia.
Yoshizawa, K. 2002. Phylogeny and higher classification of suborder Psocomorpha (Insecta: Psocodea:'Psocoptera'). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 136: 371-400.
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Valenzuela flavidus |
|---|---|
| Location | Groton, Ma. |
| Comments | 10/28/2007 |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Life Cycle Stage | adult |
| View | lateral |
| Copyright | © Tom Murray |
| Scientific Name | Valenzuela flavidus |
|---|---|
| Location | Groton, Ma. |
| Comments | 9/22/2007 |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Life Cycle Stage | adult |
| View | frontal |
| Copyright | © Tom Murray |
| Scientific Name | Xanthocaecilius quillayute |
|---|---|
| Location | Groton, Ma. |
| Comments | 10/28/2007 |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Life Cycle Stage | adult |
| View | lateral |
| Copyright | © Tom Murray |
About This Page
Emilie Bess

Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign, Illinois, USA
Kevin P. Johnson

Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign, Illinois, USA
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Emilie Bess at and Kevin P. Johnson at
Page copyright © 2009 Emilie Bess and Kevin P. Johnson
All Rights Reserved.
- First online 25 March 2009
- Content changed 25 March 2009
Citing this page:
Bess, Emilie and Kevin P. Johnson. 2009. Caeciliusidae. Version 25 March 2009 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Caeciliusidae/14467/2009.03.25 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/











 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site