Jakoba
Jakoba libera
Alastair SimpsonIntroduction
Jakoba is a group of jakobid flagellates. At present there is a single described species, Jakoba libera (Ruinen, 1938) Patterson, 1990.
Jakoba incarcerata described by Bernard et al. 2000 has now been renamed Andalucia incarcerata (Lara et al., 2006), while 'Jakoba bahamensis' / 'Jakoba bahamiensis' is not formally described. In fact, molecular phylogenies indicate that neither are specifically related to Jakoba libera (Simpson et al., 2002; Lara et al., 2006; Rodriguez-Ezpeleta, 2007; Simpson et al., 2008; Hampl et al. unpublished).
There are two cultures identified as Jakoba libera for which small subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequences are available - ATCC 50422 and WHOI DB9. The sequences are 95% identical, and are always recovered as a clade relative to other jakobids (Cavalier-Smith, 2003; Lara et al., 2006). The Jakoba libera morphospecies, so far, therefore, appears to be a clade.
Characteristics
Jakoba libera is a bacterivorous flagellate with two flagella. It is free-swimming, but often attaches to surfaces by the anterior flagellum during feeding. As in other jakobids, and many other excavates, the posterior flagellum beats within a broad ventral groove. The current generated by the flagellum draws suspended prokaryotes into the groove, where they are phagocytosed.
Jakoba libera has been reported from marine samples, and from hypersaline sites (Patterson, 1990; Ruinen, 1938).
The mitochondrial genome of Jakoba libera, while still remarkably gene-rich, includes fewer genes than other jakobid mitochondrial genomes studied to date (Gray et al., 2004). For example, only two subunits of eubacterial-type RNA polymerase are encoded by the mitochondrial genome, whereas other jakobids (e.g. Reclinomonas americana) have four mitochondrially-encoded subunits.
References
Bernard, C., Simpson, A. G. B. & Patterson, D. J. (2000) Some free-living flagellates (Protista) from anoxic habitats. Ophelia 52: 113-142.
Cavalier-Smith, T. (2003) The excavate protozoan phyla Metamonada Grasse emend. (Anaeromonadea, Parabasalia, Carpediemonas, Eopharyngia) and Loukozoa emend. (Jakobea, Malawimonas): their evolutionary affinities and new higher taxa. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53: 1741-1758.
Gray, M. W., Lang, B. F. & Burger, G. (2004) Mitochondria of protists. Annu. Rev. Genet. 38: 477-525.
Lara, E., Chatzinotas, A., Simpson, A.G.B. (2006) Andalucia (gen. nov,): a new taxon for the deepest branch within jakobids (Jakobida; Excavata), based on morphological and molecular study of a new flagellate from soil. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 53: 112-120.
O’Kelly, C. J. (1993) The jakobid flagellates: structural features of Jakoba, Reclinomonas and Histiona and implications for the early diversification of eukaryotes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 40: 627--636.
Patterson, D.J. (1990) Jakoba libera (Ruinen, 1938), a heterotrophic flagellate from deep oceanic sediments. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K. 70: 381-393.
Patterson, D.J., Vørs, N., Simpson, A.G.B. & O'Kelly, C.J. (2002) Residual and predatory heterotrophic flagellates. In: Lee, J.J., Leedale, G.F.& Bradbury P. (ed.) An illustrated guide to the protozoa, second edition. pp 1302-1328. Society of Protozoologists, Lawrence, Kansas.
Rodríguez-Ezpeleta, N., Brinkmann, H., Burger, G., Roger, A.J., Gray, M.W., Philippe, H., Lang, B.F. (2007) Toward resolving the eukaryotic tree: The phylogenetic positions of jakobids and cercozoans. Curr. Biol. 17: 1420-1425.
Ruinen J. (1938) Notizen über Salzflagellaten. II. Über die Verbereitung der Salzflagellaten. Arch Protistenkd 90: 210-258.
Simpson, A.G.B., Roger, A.J., Silberman, J.D., Leipe, D.D., Edgcomb, V.P., Jermiin, L.S., Patterson, D.J. & Sogin, M.L. (2002) Evolutionary history of “early diverging” eukaryotes: the excavate taxon Carpediemonas is a close relative of Giardia. Mol. Biol. Evol. 19: 1782-1791.
Simpson, A.G.B., Perley, T. & Lara, E., (2008) Lateral transfer of the gene for a widely used marker, alpha tubulin, indicated by a multi-protein study of the phylogenetic position of Andalucia (Excavata). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 47: 366-377.
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Jakoba libera |
|---|---|
| Comments | cell from ATCC strain 50422 |
| Source | Jakoba libera |
| Source Collection | Micro*scope |
| Image Use |
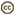 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License - Version 2.5. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License - Version 2.5.
|
| Copyright | © |
About This Page
This page is being developed as part of the Tree of Life Web Project Protist Diversity Workshop, co-sponsored by the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR) program in Integrated Microbial Biodiversity and the Tula Foundation.
Alastair Simpson

Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Alastair Simpson at
Page copyright © 2008 Alastair Simpson
 Page: Tree of Life
Jakoba . Jakoba libera .
Authored by
Alastair Simpson.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Jakoba . Jakoba libera .
Authored by
Alastair Simpson.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- First online 05 September 2008
- Content changed 05 September 2008
Citing this page:
Simpson, Alastair. 2008. Jakoba . Jakoba libera . Version 05 September 2008. http://tolweb.org/Jakoba_libera/97415/2008.09.05 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/







 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site