Stenopsychidae
Karl Kjer

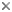
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxIntroduction
This is a small family of large and rather remarkable caddisflies, some very brightly colored, whose larvae are found in elongate tubular nets attached to rocks in the strong currents of relatively pristine rivers. The family name was established by Martynov (1926), who included the 3 genera now recognized: Stenopsyche McLachlan (ca. 80 species, widespread in the eastern Palaearctic and Oriental regions, but with 1 Afrotropical species), Stenopspychodes Ulmer (9 species from Australia), and Pseudostenopsyche Döhler (3 species from southern Chile). The family was subsequently revised by Schmid (1969). (From Holzenthal et al. 2007a)Characteristics
Larvae of several species of Stenopsyche have been described and their biology is well known (Tanida 2002, provided a detailed account). The larva has a very elongate head and sclerotized labrum with membranous margins bearing dense fringes of short setae. The labrum, with its setal brush, is apparently used to groom the tubular nets, much as is the membranous labrum of philopotamids. The diet is said to be microphagous (Lepneva 1970), but larvae of other species feed on insects as well as organic material (Tanida 2002). Larvae of Pseudostenopsyche and Stenopsyche have not been described. The adults have prominent wing patterns, often with black and golden hairs, and in some species the mouthparts are extended and the mandibles are prominent (Schmid 1969). (From Holzenthal et al. 2007a)Discussion of Phylogenetic Relationships
Frania and Wiggins (1997) found Stenopsychidae to be the sister taxon to Philopotamidae; a relationship corroborated by molecular and combined datasets (Kjer et al., 2001, Holzenthal et al., 2007b). Stenopsychodes was originally placed in Polycentropodidae, mostly because adults lack ocelli. It is now placed in its own subfamily, Stenopsychodinae. Relationships among the 3 genera have not been resolved and Pseudostenopsyche is placed in Stenopsychodinae largely because of its plesiomorphic retention of ocelli. (From Holzenthal et al. 2007a)References
Frania, H.E. & Wiggins, G.B. (1997) Analysis of morphological and behavioural evidence for the phylogeny and higher classification of Trichoptera (Insecta). Life Sciences Contributions, Royal Ontario Museum, 160, 1–67.
Holzenthal R.W., Blahnik, R.J., Prather, A.L., and Kjer K.M. 2007a. Order Trichoptera Kirby 1813 (Insecta), Caddisflies. In: Zhang, Z.-Q., and Shear, W.A. (Eds). 2007 Linneaus Tercentenary: Progress in Invertebrate Taxonomy. Zootaxa. 58 pp. 1668:639-698
Holzenthal R.W., Blahnik, R.J., Kjer K.M and Prather, A.L. 2007b. An update on the phylogeny of Caddisflies (Trichoptera). Proceedings of the XIIth International Symposium on Trichoptera. Bueno-Soria, R. Barba-Alvearz and B. Armitage (Eds). pp. 143-153. The Caddis Press.
Martynov, A.V. (1926) On the family Stenopsychidae Mart. with a revision of the genus Stenopsyche Mc Lachl. (Trichopt.). EOS-Revista Española Entomologia, 2, 281–308.
Schmid, F. (1969) La famille des stenopsychides (Trichoptera). Canadian Entomologist, 101, 187–224.
Tanida, K. (2002) Stenopsyche (Trichoptera, Stenopsychidae): ecology and biology of a prominent Asian caddisfly genus. Nova Supplementa Entomologica (Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Trichoptera), 15, 595–606.
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Stenopsychodes aureoniger |
|---|---|
| Location | New South Wales Australia |
| Creator | Karl Kjer |
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Identified By | Ralph W. Holzenthal |
| Sex | Male |
| Life Cycle Stage | Adult |
| View | Lateral |
| Collection | Univeristy of Minnesota UMSP |
| Collector | K. Kjer, F.L. Carle & J. Ware |
| Source Collection | Barcode of Life Database (BOLD) |
| Scientific Name | Stenopsychodes melanochrysus |
|---|---|
| Location | Queensland Australia |
| Creator | Karl Kjer |
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Identified By | Ralph W. Holzenthal |
| Sex | Male |
| Life Cycle Stage | Adult |
| View | Lateral |
| Collection | Univeristy of Minnesota UMSP |
| Collector | Britton & Weiner |
| Source Collection | Barcode of Life Database (BOLD) |
About This Page
Karl Kjer

Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey, USA
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Karl Kjer at
Page copyright © 2010 Karl Kjer
 Page: Tree of Life
Stenopsychidae.
Authored by
Karl Kjer.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Stenopsychidae.
Authored by
Karl Kjer.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- First online 20 July 2010
- Content changed 20 July 2010
Citing this page:
Kjer, Karl. 2010. Stenopsychidae. Version 20 July 2010 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Stenopsychidae/14567/2010.07.20 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/









 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site