Atlanta fusca
Roger R. SeapyIntroduction
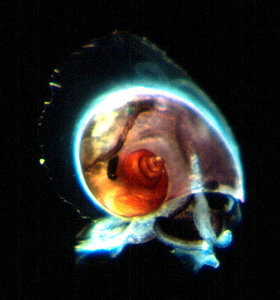
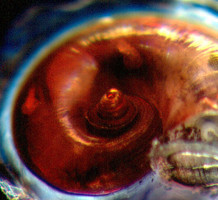
Atlanta fusca is a small species (shell diameter to 2.0 mm) that is darkly pigmented (brown to reddish-and golden-brown). The keel is tall and colorless, and inserts between the last and penultimate shell whorls in animals larger than 1.5 mm. The spire is tall and conical, consisting of 4 whorls and possessing a complex pattern of spiral sculpture that ends on the protoconch and is replaced by spiral rows of small punctae on the teleoconch. Coloration ranges from brown to amber and reddish-brown. Eyes type a, operculum type a, and radula type I. Geographic distribution is cosmopolitan in tropical to subtropical waters.
Diagnosis
- Maximal shell diameter = 2.0 mm
- Keel tall and colorless, and inserts between last and penultimate whorls in shells > 1.5 mm diameter
- Spire tall and conical, with ornate, complex sculpture
- Coloration brown to amber and reddish-brown
- Eyes type a; operculum type a; radula type I
Characteristics
- Shell
- Small, with maximal shell diameter = 2.0 mm
- Keel tall and rounded
- Keel inserts between the last and penultimate shell whorls in shells larger than 1.5 mm
-
Spire (protoconch) of four whorls, with ornate and complex surface sculpture and a prominent spiral ridge on the outer margin of the whorls that progresses in height and begins on the second whorl (see enlarged views of the two images below)
-
Spire sculpture replaced on teleoconch by spiral rows of small punctae (see enlarged view of second image below)
- Shell and spire coloration light to dark brown, amber and reddish-brown (see title illustrations and below)
- Eyes type a; lacking a transverse slit in the distal pigmented tissue
- Operculum type a (macro-oligogyre)
- Radula type I, small and ribbon shaped. Like Atlanta turriculata, each tooth row includes (1) a monocuspid central tooth, with a postero-lateral process on each side of the tooth, (2) biscuspid lateral teeth, each with a strong rectangular process on the inner side, and (3) a monocuspid marginal tooth
- Larva
- The two lobes of the velum in early larvae give rise to the six-lobed velum in late larvae
 Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window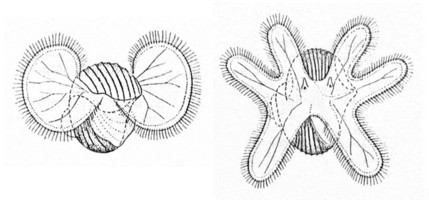
Figure. Early (left) and late (right) stage larvae of Atlanta fusca. Drawings combined from Franc (1948, Figs. 10, 11). © 1948 A. Franc

Figure. Late veliger larva of Atlanta fusca with six, ciliated velar lobes. Scale bar = 0.5 mm. Modified from Richter (1968, Fig. 11). © 1968 G. Richter
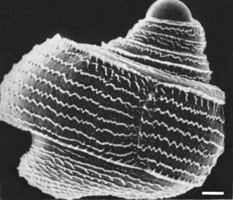
- Surface sculpture of larval shell (following the apical embryonic portion) of multiple, parallel spiral ridges
 Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
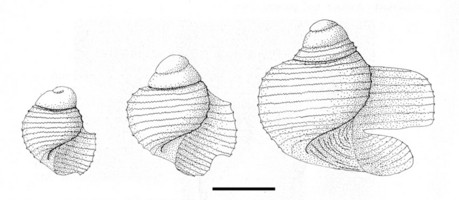
Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new windowFigure. Larval shell of Atlanta fusca. Left: Scanning electron micrograph of shell viewed in the shell plane. Scale bar = 50 µm. Modified from Thiriot-Quiévreux (1973, Fig. 6b). © 1973 C. Thiriot Right: Sketches of three stages in the development of the larval shell. Scale bar = 250 µm. Modified from Richter (1968, Fig. 10). © 1968 G. Richter
- The two lobes of the velum in early larvae give rise to the six-lobed velum in late larvae
Comments:
Atlanta fusca is a cosmopolitan species, found at tropical to subtropical latitudes. It is limited to the upper 100 m of the water column in Hawaiian waters (Seapy, 1990b). Comparison of day and night vertical distribution of abundances suggested that a portion of the population from 50-100 m migrated into the upper 50 m at night
References
Franc, A. 1948. Veligeres et mollusques gasteropodes des Baies d'Alger et de Banyuls. Journal de Conchyliologie (Paris) 88:13-35, plates 1 and 2.
Richter, G. 1968. Heteropoden und Heteropodenlarven im Oberfl?chenplankton des Golfs von Neapel. Pubblicazioni della Stazione Zoologica di Napoli 36: 346-400.
Richter, G. and R. R. Seapy. 1999. Heteropoda, pp. 621-647. In: D. Boltovskoy (ed.), South Atlantic Zooplankton. Leiden: Backhuys Publ.
Seapy, R. R. 1990a. The pelagic family Atlantidae (Gastropoda: Heteropoda) from Hawaiian waters: a taxonomic survey. Malacologia 32: 107-130.
Seapy, R. R. 1990b. Patterns of vertical distribution in epipelagic heteropod molluscs off Hawaii. Marine Ecology Progress Series 60: 235-246.
Thiriot-Quievreux, C. 1973. Heteropoda. Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review, H. Barnes (ed.) 11: 237-261.
Title Illustrations

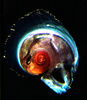
| Scientific Name | Atlanta fusca |
|---|---|
| Location | Hawaiian waters |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Sex | Male |
| Life Cycle Stage | adult |
| View | right side |
| Image Use |
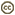 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
©

|
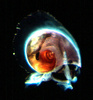
| Scientific Name | Atlanta fusca |
|---|---|
| Location | Hawaiian waters |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Sex | Male |
| Life Cycle Stage | adult |
| View | right side, tilted |
| Image Use |
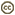 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
©

|
About This Page

California State University, Fullerton, California, USA
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Roger R. Seapy at
Page copyright © 2008
 Page: Tree of Life
Atlanta fusca .
Authored by
Roger R. Seapy.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Atlanta fusca .
Authored by
Roger R. Seapy.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- First online 15 December 2008
- Content changed 15 January 2009
Citing this page:
Seapy, Roger R. . 2009. Atlanta fusca . Version 15 January 2009 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Atlanta_fusca/28759/2009.01.15 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/









 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site