Rhinophrynidae
David Cannatella- Rhadinosteus parvus

- Chelomophrynus bayi

- Rhinophrynus
- Rhinophrynus dorsalis
- Rhinophrynus sp.

- Eorhinophrynus

Note: this taxon list is still under construction. It does not yet contain all known Rhinophrynidae subgroups.
Introduction
The Mexican Burrowing Toad (Rhinophrynus dorsalis) is the only living member of this family. This toad's type of tadpole (Orton Type 1) is evidence of a close phylogenetic relationship between Rhinophrynidae and Pipidae. The larger group to which these two families, and the fossil family Palaeobatrachidae, belong is called the Pipoidea.
Definition of the name Rhinophrynidae and thus a listing of synapomorphies for the taxon is problematic because the name Rhinophrynidae has been applied consistently to several fossil taxa (Henrici, 1991) that are related to the single living taxon Rhinophrynus dorsalis. Association of the name Rhinophrynidae or even Rhinophrynus with living taxa only would render those names redundant with the name of the living species. Because the living taxon has a widely used name, we use the more inclusive names Rhinophrynus and Rhinophrynidae for taxa that incorporate fossils. This also has the advantage of stabilizing those names with their common usage. Therefore, Rhinophrynidae is defined to be a stem-based name for those pipoids that are more closely related to the taxon dorsalis than to †Palaeobatrachidae + Pipidae. Rhinophrynus is defined as a stem-based name for rhinophrynids that are more closely related to the living taxon dorsalis than to †Eorhinophrynus or †Chelomophrynus.
Maxson and Daugherty (1980) reported MC'F distances of 170 between Ascaphus and Rhinophrynus dorsalis, more than 190 between Rhinophrynus and Bombina, and more than 200 between Rhinophrynus and Xenopus, Scaphiopus, Pelobates, and three neobatrachians. From these data they tentatively concluded that "... Rhinophrynus appears to have shared a common ancestor more recently with Ascaphus than with other salientian lineages..." (p. 279). This is in contrast to the conclusions reached by Cannatella (1985) and Hay et al. (1995).
Characteristics
By the above definition, synapomorphies of Rhinophrynidae include (1) the division of the distal condyle of the femur into lateral and medial condyles, (Henrici, 1991), and three others that we derived from Henrici's work: (2) modification of the prehallux and distal phalanx of the first digit into a spade for digging, (3) tibiale and fibulare short and stocky, with distal ends fused, and (4) an elongate (at least as long as wide) atlantal neural arch. The first three of these are unknown in †Eorhinophrynus. Synapomorphies of Rhinophrynus are given by Henrici (1991).
References
Cannatella, D. C. 1985. A phylogeny of primitive frogs (archaeobatrachians). Ph.D. Dissertation, The University of Kansas, Lawrence.
Hay, J. M., I. Ruvinsky, S. B. Hedges, and L. R. Maxson. 1995. Phylogenetic relationships of amphibian families inferred from DNA sequences of mitochondrial 12S and 16S ribosomal RNA genes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 12(5):928-937.
Henrici, A. C. 1991. Chelomophrynus bayi (Amphibia, Anura, Rhinophrynidae), a new genus and species from the Middle Eocene of Wyoming: Ontogeny and relationships. Ann. Carnegie Mus. 60:97-144.
Maxson, L. R., and C. H. Daugherty. 1980. Evolutionary relationships of the monotypic toad family Rhinophrynidae: a biochemical perspective. Herpetologica 36:275-280.
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Rhinophrynus dorsalis |
|---|---|
| Image Use |
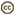 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 1995 David Cannatella

|
About This Page
David Cannatella

University of Texas, Austin, Texas, USA
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to David Cannatella at
Page copyright © 1995 David Cannatella
 Page: Tree of Life
Rhinophrynidae.
Authored by
David Cannatella.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Rhinophrynidae.
Authored by
David Cannatella.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- Content changed 25 November 2008
Citing this page:
Cannatella, David. 2008. Rhinophrynidae. Version 25 November 2008 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Rhinophrynidae/16982/2008.11.25 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/







 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site