Lakota name: hu ciήśќá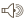 Listen to Lakota Plant Name: hu ciήśќá
Listen to Lakota Plant Name: hu ciήśќá
Scientific name: Asclepias viridiflora
Common name: Green comet milkweed
Historical use as a medicinal plant by the Lakota or any other Culture: The Lakota tribe had many medicinal uses for the Green Comet Milkweed. The roots of this plant are applied to the gums of babies to alleviate pain. They are also chewed by people who are suffering from diarrhea. The plant was used the help women in lactating. It was given to them to increase milk production. It has no current medicinal uses. The roots were stored for winter, when they would be used in spice soups.
Federal Status: Currently the US government has not posted this species as endangered. However, Conneticut, Florida, and New York have marked it as being threatened or of special concern. Based off the population and growth of these states in recent years, I am led to believe that housing developments might be at least one reason for their plight.
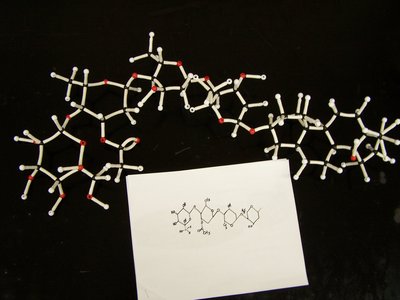
Description: A. viridiflora range in height from 1 to 3 feet. The flowers are approximately 1/4 inch across. This plant is native to the United States. Its leaves typically have an acuminate1 shape with an acute2 tip. It has opposite3 leaves that have a simple4 structure. It was commonly used by the Lakota and was given the name "hu ciήśќá" which means "spoon shaped leaf".
- 1 A long slender leaf, tapering to a point
- 2 Angle of less than 90 degrees
- 3 Leaves attach to the stem in pairs
- 4 Leaves are one, unseperated blade



Asclepias viridiflora. Left: branch with flowers © Richard Old, XID Services, Inc., United States Right: flowers © 2004
Similar Species: The green comet milkweed is part of the genus Asclepias, which has at least 140 species. All of these species are considered milkweeds. The reason why they are called milk weeds is because of their secondary compounds that have a milk and water mixture look.
Secondary Compound: Cardiac Glycosides. Cardiac Glycosides work by slowing the sodium-potassium pump in heart cells. This increases sodium ions in the cell which causes an increase in calcium ions. This increase in calcium increases the functionality of the cell.

Molecular structure of a cardiac glycoside. © 1sagebrush9
Flowering Period: The flowering period of this plant is from June to September. The flowers of this plant are very distinct, making the plant easy to pick out during its flowering period; however, during the rest of the year it blends in with its surrounding plants.
Habitat:
- Dry Areas
- Prairies
- Woods
- Inland Sands
- Barren Areas
- Sandy Soil

 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site