Abacetini
Kipling Will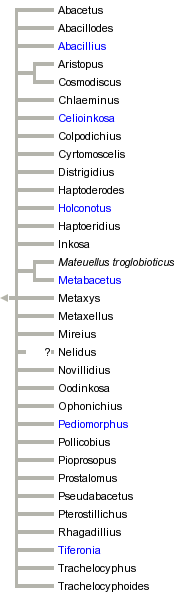

This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxIntroduction
Abacetini is a group of probably more than 500 species for which there is little modern synthesis or taxonomic revision. The group is distributed throughout Africa and into southern Europe, across tropical and subtropical Asia and into the Pacific as far as northern Australia.Characteristics
A broad set of taxa have been informally associated with Abacetus based on the combination of the lack of the angular base of stria 1; a single pair of deeply impressed, linear basal impressions of the pronotum; a single or no dorsal puncture on the third elytral interval; the basal elytral puncture at or near stria two and males with symmetrically expanded protarsomeres. Additionally, nearly all of these taxa have deeply impressed, elongate frontal impressions on the head; sinuate anterior coxal sulcus and coiled spermatheca.The most obvious characteristic and likely synapomorphy for a possibly dervied clade (Abacetini s.str.) is the eccentrically inserted second antennomere and, perhaps, the strongly transverse mentum. The mentum form, however, is somewhat variable. DNA sequence data also supports this clade based on a selected set of exemplars and several gene loci (K.Will unpublished).Title Illustrations
| Scientific Name | Abacetus sp |
|---|---|
| Location | Vietnam |
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Identified By | K.Will |
| Life Cycle Stage | Adult |
| Body Part | Habitus |
| View | Dorsal |
| Collection | AMNH |
| Copyright |
© Kipling Will

|
| Scientific Name | Celioinkosa kivuana |
|---|---|
| Life Cycle Stage | Adult |
| Copyright |
© Kipling Will

|
About This Page
Kipling Will

University of California, Berkeley, California, USA
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Kipling Will at
Page copyright © 2005 Kipling Will
- First online 07 July 2006
- Content changed 07 July 2006
Citing this page:
Will, Kipling. 2006. Abacetini. Version 07 July 2006 (temporary). http://tolweb.org/Abacetini/51300/2006.07.07 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org








 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site